Faceting
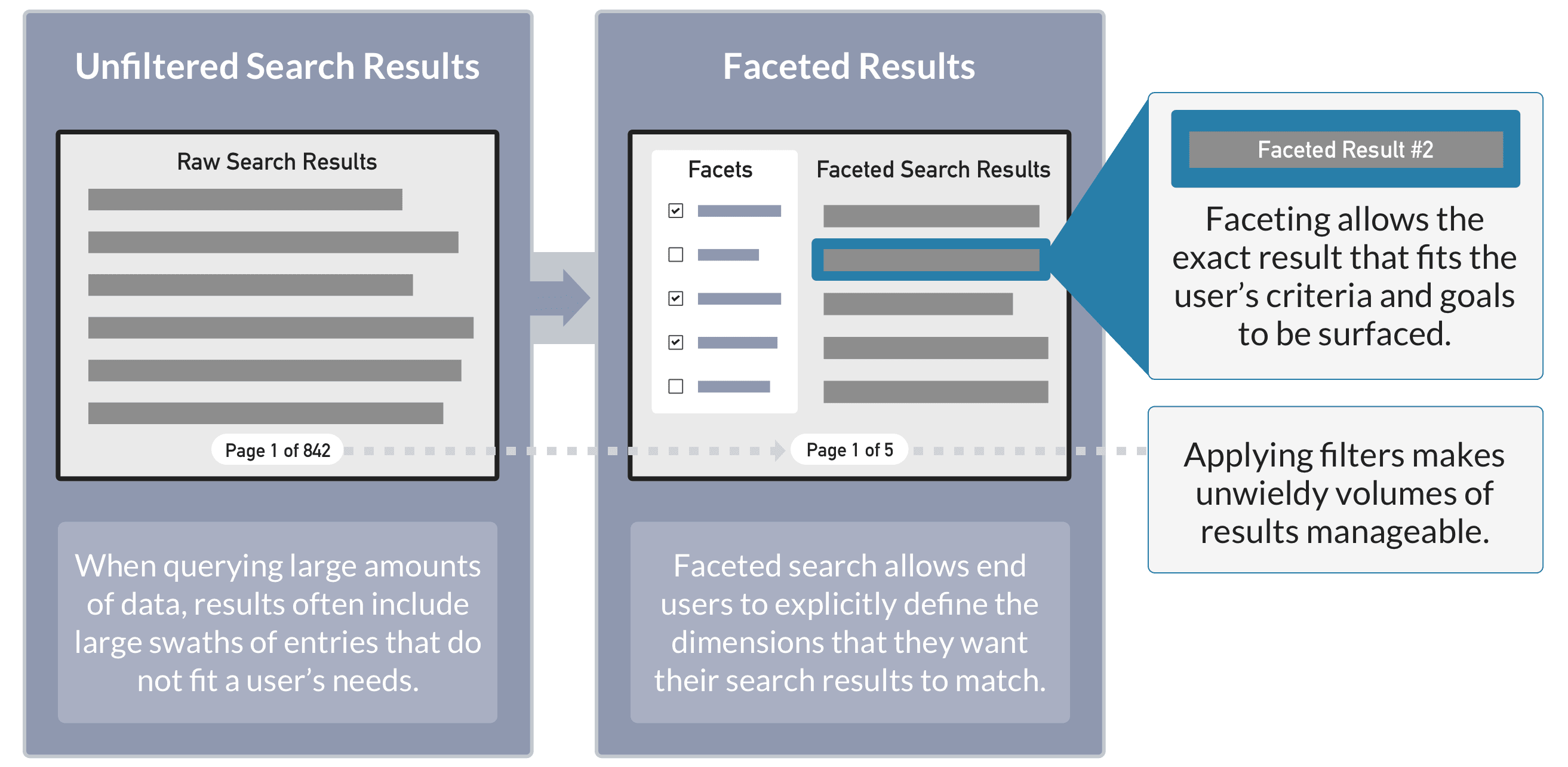
Faceting is the name given to a set of computed counts over a search result returned together with the documents which match the search query. Facets are most often used to create additional navigational controls on the search results page or panel. Users can expand and restrict their search criteria in a natural way, without having to construct complicated queries. For example, popular e-commerce facets include product category, price range, availability, and user ratings.
Fusion leverages Solr’s Faceting search components.
Field faceting
In Solr the most straightforward kind of faceting is field faceting, in which Solr’s FacetComponent computes the top values for a field and returns the list of those values along with a count of the subset of documents in the search results which match that term. Field faceting works best over fields which contain a single label or set of labels from a finite, controlled lexicon such as product category. Fusion’s Facet Query Stage can be used to configure field faceting as part of the search query pipeline.
Range faceting
Range facets are used for fields which contain date or number values. Values can be grouped into ranges by specifying additional query parameters.
To configure range faceting, use the Additional Query Parameters Stage to specify Solr range faceting parameters.
JSON faceting
In eCommerce, one product often contains multiple SKUs. In this case, it’s ideal to group search results on the product ID, such that only one result for all SKUs of a given product will be returned. This is achieved by using the unique parameter in JSON facets. You can use JSON facets by creating Query Params in a Query Profile or with the Additional Query Parameters Stage in a Query Pipeline.
JSON faceting example
For example, if a product is available in SKUs of multiple colors, the following should apply:
-
All available colors (in any SKU in the result set) are represented in the facets
-
The
countfor those facets reflects matching product counts, not SKU counts.
In this example, eight SKU records are used across two products.
| SKU | Product | Color |
|---|---|---|
Sku11 |
Prod1 |
Red |
Sku12 |
Prod1 |
Blue |
Sku13 |
Prod1 |
Blue |
Sku14 |
Prod1 |
Blue |
Sku21 |
Prod2 |
Red |
Sku22 |
Prod2 |
Blue |
Sku23 |
Prod2 |
Green |
Sku24 |
Prod2 |
Green |
With the preceding data, the color facet should show:
Color: Red (2) Blue (2) Green (1)
Facet stats
The Stats component is useful for computing statistics against fields within your document set. For example, when performing a query, you can invoke the Stats component to return information about the mean price of a product or determine how many documents are missing a particular field.
Facet stats example
https://FUSION_HOST:FUSION_PORT/api/apps/exampleapp/query/examplepipeline/select?q=Cooking&stats=true&stats.field=price
...
"stats":{
"stats_fields":{
"price":{
"min":12.34,
"max":57.65,
"mean":34.56,
...Faceting concepts
Key Facet Concepts:
- Term
-
A specific value from a field.
- Limit
-
The maximum number of terms to be returned.
- Offset
-
The number of top facet values to skip in the response (just like paging through search results and choosing an offset of 51 to start on page 2 when showing 50 results per page).
- Sort
-
The order in which to list facet values:
countordering is by documents per term, descending, andindexordering is sorted on term values themselves. - Missing
-
The number of documents in the results set which have no value for the facet field.
- Choice of facet method
-
(advanced) Specify Solr algorithm used to calculate facet counts. (See Facet Method Configuration for details). One of:
-
enum. Small number of distinct categories. -
fc("field cache"). Many different values in the field, each document has low number of values, multi-valued field. -
fcs("single value string fields"). Good for rapidly changing indexes.
-
Additional resources
-
View our training on Faceting.