Signals Types and Structures
Signals can be broadly categorized as implicit or explicit. When signals are enabled, Fusion produces several built-in signal types by default, all of which are implicit signals. You can also create custom signal types, including explicit signals. Be sure to verify that your signals include all of the important fields for best results. It is also useful to rank your signal types in terms of how strongly each type indicates a user’s interest in an item.
Implicit signals vs explicit signals
Signals can reveal a user’s level of interest in an item in two main ways:
-
Implicit
The user shows interest by engaging with the item/document through clicks, searches, and so on. Since this type of interaction requires no additional effort on the user’s part, these types of signals tend to be plentiful. They can be used to infer a measurable value of interest in order to build an accurate recommender system.
-
Explicit
An explicit signal is created when a user intentionally assigns a clear, measurable value to an item, such as by giving it a rating. This value can be used to rank items, for example. Since this requires the user to invest extra time to provide the information, the number of ratings tends to be small compared to the total number of users interacting with the item.
You can create recommendations based on implicit signals out of the box. For recommenders based on explicit signals, contact your Lucidworks Professional Services representative.
Built-in signal types
There are five built-in signal types:
Annotation signals are generated when a user bookmarks, likes, or comments on a document. Annotation signals are likewise generated when the user removes a bookmark, like, or comment.
|
|||
Login signals record information about specific users when they log in to an application. This includes a time stamp and various session details. |
|||
A request signal is generated by a front-end search app and captures the raw user query and other contextual information about a user and their journey through the search app. |
|||
Response signals are automatically generated by a query pipeline when the signals feature is enabled for a collection. |
|||
Click signals are generated when a user clicks on a page element that is being monitored by the search app. Click signals are sent from the search app to Fusion. |
| Because response signals and their fields are automatically generated, this topic does not cover what response signal fields are required. |
Annotation signals
Annotation signals are generated when a user bookmarks, likes, or comments on a document. Annotation signals are likewise generated when the user removes a bookmark, like, or comment.
| Annotation signals are generated by App Studio. If you are not using App Studio, this type of signal is not relevant to your search application. |
Login signals
Login signals record information about specific users when they log in to an application. This includes a time stamp and various session details.
Request signals
A request signal is generated by a front-end search app and captures the raw user query and other contextual information about a user and their journey through the search app. The request signal contains no information about the documents the user searched for.
A request signal should have the following fields:
[
{
"id":"288fe4f7-6680-403e-8d18-27647cdd9989",
"timestamp":1518717749409,
"type":"request",
"params":{
"user_id":"admin",
"session":"ef4e00cd-91bb-45b4-be80-e81f9f9c5b27",
"query":"USER QUERY HERE",
"app_id":"SEARCH APP ID",
"ip_address":"0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1",
"host":"Lucids-MacBook-Pro-5.local",
"filter":[
"field1/value",
...
],
"filter_field":[
"field1"
]
}
}
]Additional optional fields are used by App Insights. In the raw signal, optional fields should be inside the params object. Optional fields are as follows:
"page_title":"Fusion Search",
"path":"/search",
"browser_type":"Browser",
"browser_version":"64.0.3282.140",
"browser_name":"Chrome",
"referrer":"http://localhost:8080/",
"ctx_prev_uri":"/",
"ctx_prev_query":"",
"ctx_prev_path":"/",
"os_manufacturer":"Apple Inc.",
"os_name":"Mac OS X",
"os_id":"778",
"os_device":"Computer",
"os_group":"Mac OS X"Response signals
Response signals are automatically generated when a query pipeline receives a search request and that request is processed. This occurs only when the signals feature is enabled for a collection.
| Front-end search applications should not send response signals to Fusion directly, as those would conflict with the auto-generated signals. |
Response signals capture much of the same information as a request signal. Response signals also capture information about the actual results returned to the front-end search application, such as the search query, the query state (including sorts, pagination, and applied filters) and all the results from Fusion that are related to the query. Response signals can also identify search requests that returned no results to the user or requests that resulted in no clicks from the user.
Fusion creates a unique fusion-query-id to each response signal. This is used to correlate the downstream click signals with the original search request. After a user receives the results from their search, they can interact with the documents. In order to know which results (if any) were shown to the user, we use the response signals correlated with the unique fusion-query-id.
A response signal has the following explicit fields, plus any additional query parameters sent by the search application for a query:
| Field Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
The x-fusion-query-id generated by the query-pipeline used for associating click signals with queries in experiments and aggregation jobs. |
|
|
Signal type |
|
|
Used by Insights to determine if this query had results or was empty |
|
|
User session ID; the search app should pass the session ID in the query params for a query |
|
|
The actual query string sent to Solr from Fusion |
|
|
The incoming query from the search app before it is enriched by the query pipeline |
|
|
A hash generated from the session, query, and filters fields; used as a rollup key in Insights to group activity by a specific |
|
|
Filter queries sent to Solr; the Fusion SearchLogger component combines multiple fq parameters into a single value delimited by " $ " |
|
|
Reformatted filter queries |
|
|
User ID; the search app should pass the user_id in the query params |
|
|
A comma-delimited list of document IDs returned for the page of results; this field is used by Fusion Spark jobs, such as the ground truth job, to perform click/skip analysis |
|
|
Fusion query pipeline that processed this query |
|
|
Fusion collection |
|
|
Query time from Solr, in milliseconds |
|
|
Number of rows requested for this query |
|
|
Total number of documents matching the query |
|
|
Total processing time of this query in milliseconds, includes Solr qtime and Fusion query processing time |
|
|
Timestamp when the query request was received by Fusion |
|
|
Offset of results; this field is used by experiment metrics to calculate MRR |
|
|
Position of the clicked result within the list of results |
|
|
Any other query param sent from the search app to Fusion that was not already mapped to a declared field |
|
Fusion’s experiment framework relies heavily on response signals and the linking between response and clicks signals using the fusion_query_id.
Click signals
Click signals are explicit events that capture any type of user interaction that the business is interested in keeping track of. The basic click signal records the action of a user clicking an item in a context, whether that context is within search results, category browse, type ahead suggestions, or other locations. Each unique action receives a name such as click2pdp, add2cart or purchase.
When a user clicks a search result, your search app should send a click signal to Fusion. All click signals should include a fusion_query_id field pulled from the query response header x-fusion-query-id.
In addition, click signals should include the following fields:
[
{
"id":"SOME UUID HERE",
"timestamp":1518725351750,
"type":"click",
"params":{
"fusion_query_id":"ABkaEA11",
"user_id":"admin",
"session":"b3a15101-9e30-4e28-8a23-d1f663c2ee06",
"query":"tiger woods",
"ctype":"result",
"res_offset":0,
"filter":[
"type/Game"
],
"ip_address":"0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1",
"host":"Lucids-MacBook-Pro-5.local",
"doc_id":"9502308",
"app_id":"SEARCH APP ID",
"res_pos":1,
"filter_field":[
"type"
]
}
}
]Additional optional fields are used by App Insights. In the raw signal, optional fields should be inside the params object. Optional fields are as follows:
"browser_type":"Browser",
"browser_version":"64.0.3282.140",
"browser_name":"Chrome",
"referrer":"http://localhost:8080/",
"ctx_prev_uri":"/",
"ctx_prev_query":"",
"ctx_prev_path":"/",
"os_manufacturer":"Apple Inc.",
"os_name":"Mac OS X",
"os_id":"778",
"os_device":"Computer",
"os_group":"Mac OS X"
"url":"http://localhost:8080/#/product/9502308",
"label":"Tiger Woods PGA Tour 09 All-Play - Nintendo Wii",Custom signal types
The signal type parameter can also take arbitrary values for custom signal types. For example, these custom events are important for e-commerce sites:
-
Add-to-favorites
-
Add-to-cart
-
Remove-from-cart
-
Purchase
-
Hover/quick-view
To collect custom signals, configure your front-end search application to send signals to Fusion using a custom value for the type field. Custom signals should also include the fields described below in order to get the best results from aggregation and recommendation jobs.
To use custom signals in recommendations, you must add them to the value of the signalTypeWeights parameter in the configuration for the COLLECTION_NAME_user_item_preferences_aggregation job and the COLLECTION_NAME_user_query_history_aggregation job.
Custom signals can be analyzed in App Insights just like pre-defined signal types.
Required signal fields
Depending on how you use signals, certain fields are required. These are signals collection field names and not the JSON field names in the in-bound signals document. An example is when sending the user id, write it as params.user_id.
The fields mentioned in this section are defined as follows:
| Field Name | Example Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Number of times an interaction event occurred with this item |
|
NMDDV |
Product ID or Item ID |
|
xwearabletech |
A query string from the user |
|
91aa66d11af44b6c90ccef44d055cf9a |
Id for session in which user generated the signal |
|
quick_view_click |
Type of session the user used to interact with the platform |
|
11506893 |
ID of user during the session |
|
2018-11-20T17:58:57.650Z |
Time when signal was generated |
Some signal types, including custom signal types, may include additional fields.
Required fields by use case
Aggregations, recommendations, and App Insights work best when certain fields are present in your signals. See these topics for details:
Required fields by signal type
The following table describes which fields are required for annotation, click, login, and request signals.
| Requests (or queries) can also require additional, available user data for the search. |
| Field | Type | Description | Example | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
string |
Unique ID for the signal. |
|
✅ Annotation ✅ Click ✅ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Product ID or Item ID of the clicked result. |
|
✘ Annotation ✅ Click ✘ Login ✘ Request |
|
timestamp |
Timestamp of when the signal was generated. This timestamp follows Unix epoch time formatting. |
|
✅ Annotation ✅ Click ✅ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Unique ID for the user that generated the signal. |
|
✅ Annotation ✅ Click ✅ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Unique ID for the user’s browser session. |
|
✅ Annotation ✅ Click ✅ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Host name of the server which is hosting the app that is generating the signal. |
|
✅ Annotation ✅ Click ✅ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
IP address of the user that generated the signal. |
|
✅ Annotation ✅ Click ✅ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Name of the application that is generating the signal. |
|
✅ Annotation ✅ Click ✅ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Type of the annotation signal, either "comment", "bookmark", or "like". Required fields for "comment":
Required fields for "bookmark":
Required fields for "like":
|
|
✅ Annotation ✘ Click ✘ Login ✘ Request |
|
string |
Terms of the query. |
|
✘ Annotation ✅ Click ✘ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Unique ID for the |
|
✘ Annotation ✅ Click ✘ Login ✘ Request |
|
array of string |
List of filters associated with the query, which in turn is associated with signal. |
|
✘ Annotation ✅ Click ✘ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Type of click. |
|
✘ Annotation ✅ Click ✘ Login ✘ Request |
|
number |
Position of the clicked result within the list of results. |
|
✘ Annotation ✅ Click ✘ Login ✘ Request |
|
number |
Result page. |
|
✘ Annotation ✅ Click ✘ Login ✘ Request |
|
string |
URL of the page that the signal originated from. |
|
✘ Annotation ✘ Click ✘ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
URL path of the page that the signal originated from. |
|
✘ Annotation ✘ Click ✘ Login ✅ Request |
|
string |
Title of the page that the signal originated from. |
|
✘ Annotation ✘ Click ✘ Login ✅ Request |
Field name suffixes
Fusion can add suffixes when fields are indexed. This table lists common suffix values.
| Single Value Suffix | Multivalued Sufix | Type |
|---|---|---|
|
|
boolean |
|
|
double |
|
|
date |
|
|
float |
|
|
int |
|
|
long |
|
|
string |
|
|
text |
Signal field count analysis
Lucidworks recommends performing signal field count analysis to determine whether any of the fields above are missing from some of your signals.
The table below shows how to query for specific fields using the Query Workbench in order to compare the number of results for each field with the total number of documents in the signals collection. In the examples in the third column, some fields appear in all 33,477,919 signals documents, while others appear in fewer documents.
| Field name | Query | Example number of documents |
|---|---|---|
|
|
33,477,919 |
|
|
11,101,165 |
|
|
23,216,297 |
|
|
33,477,919 |
|
|
19,724,598 |
|
|
11,101,165 |
|
|
33,477,919 |
|
|
26,117,399 |
|
|
26,117,399 |
You can also get the number of signals documents that contain all of the required fields by using the following query:
count_i:[* TO *] doc_id:[* TO *] id:[* TO *] query:[* TO *] type:[* TO *] user_id:[* TO *] timestamp_tdt:[* TO *] session_id:[* TO *]The query_id field
For each incoming signal, Fusion calculates a value for the query_id field.
App Insights uses to create group-by-query reports like the one shown below:
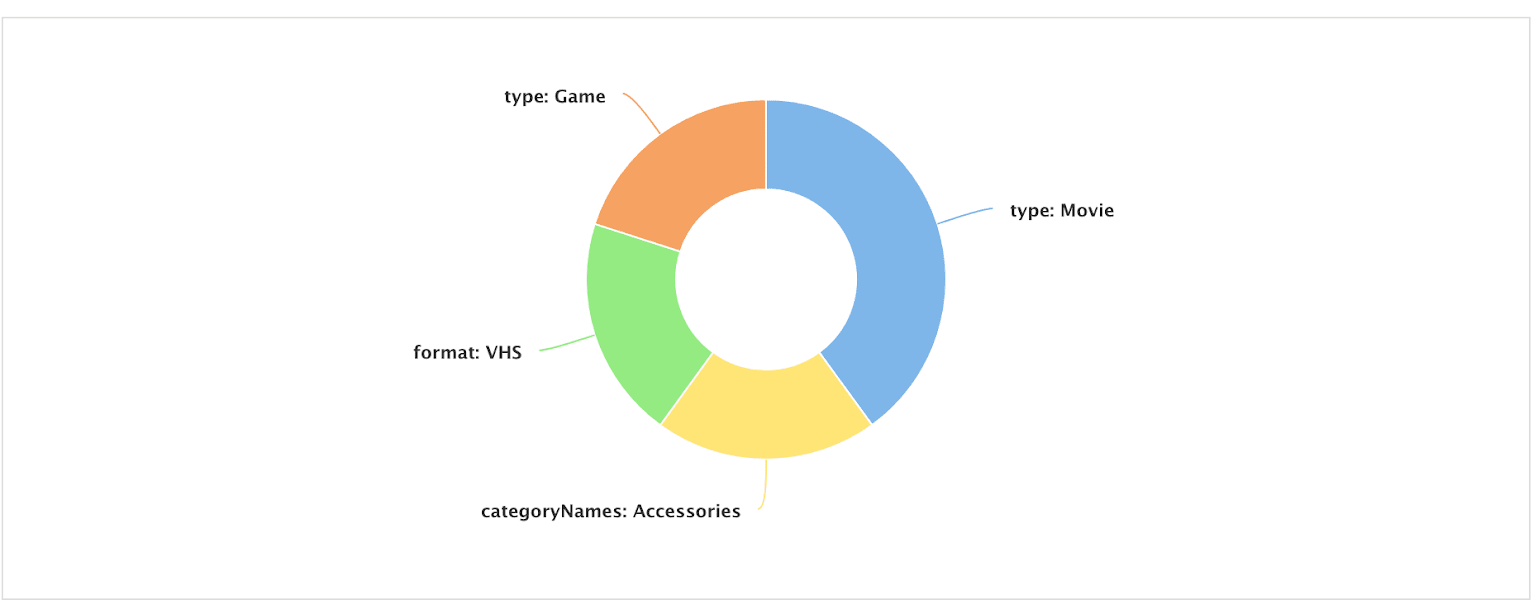
The query_id field should not be confused with the fusion_query_id, which is a unique ID for each query processed by a Fusion query pipeline, or with query_s which is the query string.
|
To calculate the value, Fusion creates a hash based on session, query, and filter fields, then saves it into the query_id field.
The filter field can either be passed in by the search app,
or computed by the SignalFormatterStage (the first stage in the _signals_ingest pipeline) using the raw filter queries. For instance, on a response signal that is generated by a query pipeline, the following fq query params get translated into the multi-valued filter field:
-
Raw query parameters:
fq={!tag=format}format:(VHS)&fq={!tag=type}type:(Movie) -
filters_sfield (created by the SearchLogger component):{!tag=format}format:(vhs) $ {!tag=type}type:(movie) -
filterfield:"filter":["format/VHS", "type/Movie"]
App Insights uses the filter field to generate various reports.
Signal type ranking
When you have defined some custom fields, it is useful to rank them according to how strongly they indicate a user’s interest in an item. While it’s not necessary to exclude certain signal types from the main signals collection, some can be excluded from signal aggregations in order to focus on the most important fields when generating recommendations.