Ingest and Indexing
Data Ingestion
Data ingestion gets your data into Fusion Server, and data indexing stores it in a format that is optimized for searching. These topics explain how to get your data into Fusion Server in a search-optimized format.
Collections
Collections are a way of grouping data sets so that related data sets can be managed together. Every data set that you ingest belongs to a collection. Any app can contain one or more collections. See Collection Management.
Datasources
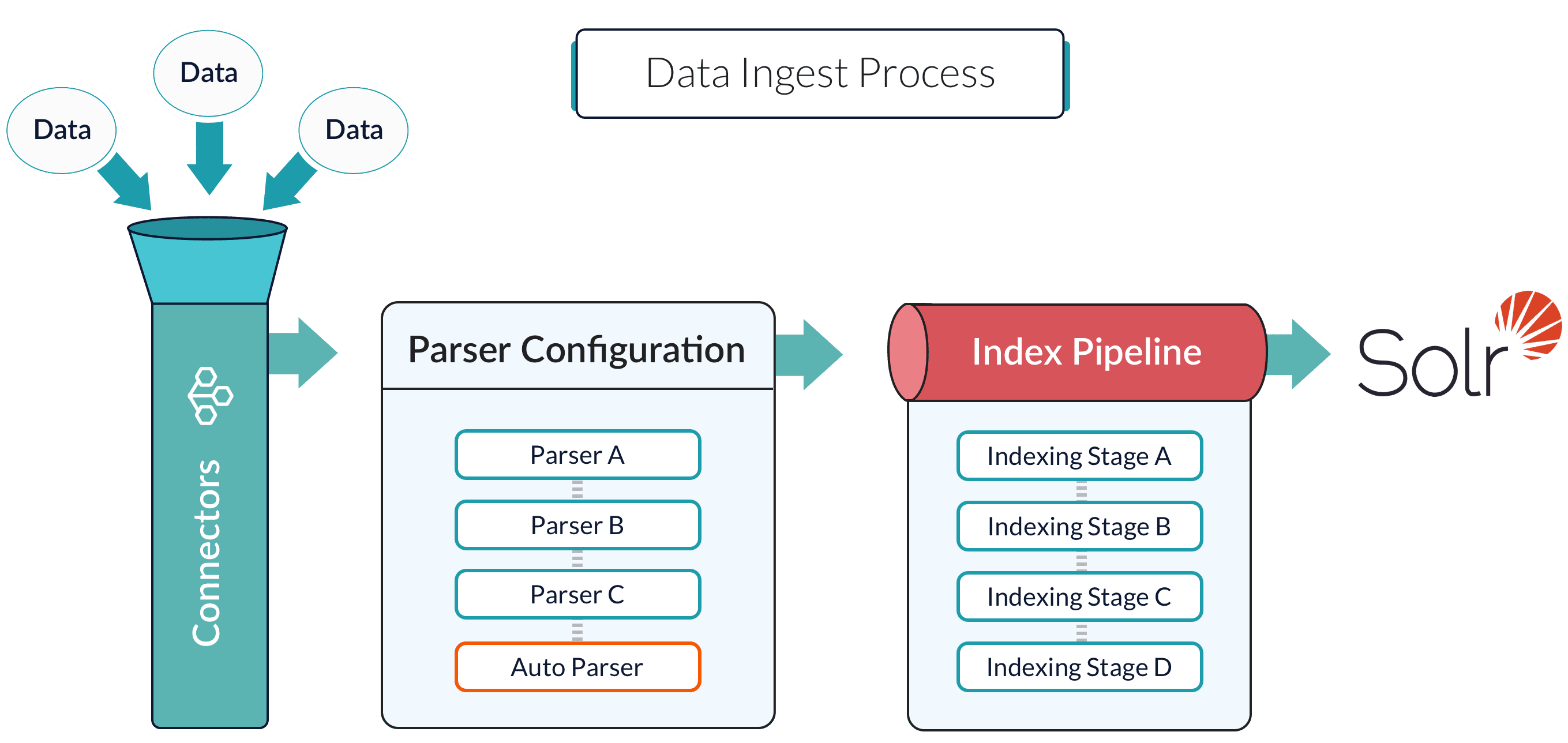
Datasources are configurations that determine how your data is handled during ingest by Fusion Server’s connectors, parsers, and index pipelines. When you run a fully-configured datasource, the result is an indexed data set that is optimized for search, depending on the shape of your data and how you want to search it. See Datasource Configuration.
Connectors
Connectors are Fusion components that ingest and parse specific kinds of data. There is a Fusion connector for just about any data type.
Blob storage
Blob storage is a way to upload binary data to Fusion Server. This can be your own data, such as images or executables, or it can be plugins for Fusion Server, such as connectors, JDBC drivers, and so on.
Other methods
In some cases, you might find that it is best to use other ingestion methods, such as the Parallel Bulk Loader, Hive, Pig, or pushing data to a REST API endpoint.
Batch ingestion of signals is also available with a Fusion AI license.
Indexing
Indexing converts your data into an indexed collection in Fusion’s Solr core. It is critical for ensuring that your data is stored in a format that is ideal for your search application.
-
Index pipelines determine the details of the conversion.
-
Index pipeline stages are the building blocks of index pipelines.
-
The Index Workbench is Fusion’s index pipeline development tool.